Dendrobium Officinale and Spermidine: The Golden Duo for Anti-Aging and Longevity
In traditional Chinese medicine, Dendrobium officinale is hailed as a “national treasure” for its myriad health benefits, including extending lifespan, antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory effects, immune enhancement, metabolic regulation, cell regeneration and repair, blood sugar reduction, and even cancer prevention. It’s no wonder that this precious herb is highly sought after, with prices ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per pound, depending on its quality.
The active components of Dendrobium officinale include polysaccharides, alkaloids, and amino acids, with Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide (DOP) accounting for 36.3% of its composition, making it the primary active ingredient responsible for the herb’s medicinal effects. Research indicates that DOP exerts its anti-aging effects primarily by modulating the immune system and gut microbiota.
To maximize the anti-aging and longevity benefits, scientists at Jiangnan University explored the combination of this traditional Chinese medicine with a rising star in the anti-aging field: spermidine. Spermidine, a type of polyamine, helps regulate cellular self-cleaning and repair processes, as well as the body’s perception of nutrients, thereby contributing to anti-aging, muscle mass enhancement, and metabolic improvement. The two substances, though distinct in their mechanisms, work through different pathways to achieve their effects.
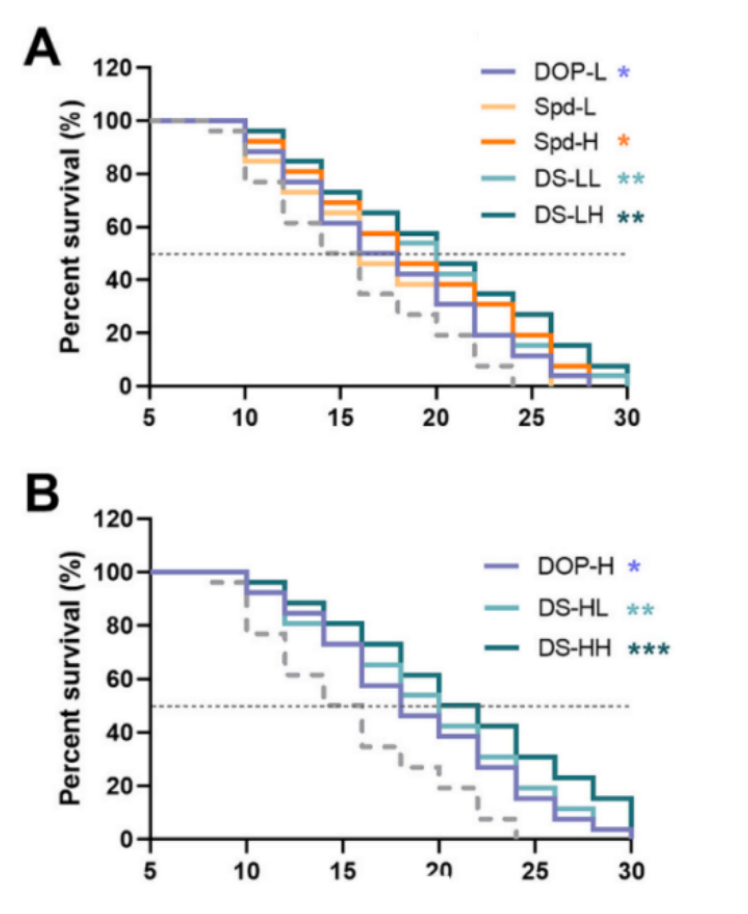
The researchers set out to find the optimal dosage combination of DOP and spermidine. The results were striking: the high-dose combination of DOP and spermidine (DS-HH) showed the most significant improvement in lifespan, with a median life extension of 40% in nematodes!
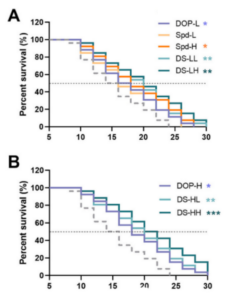
Moreover, the DS-HH group exhibited enhanced resistance and mobility. Under oxidative stress, the median survival time of the DS-HH group was nearly double that of the control group, demonstrating superior antioxidant capabilities. In heat stress tests, the DS-HH group also showed the best heat resistance. Additionally, the DS-HH group showed significant improvements in body bending and head movement, indicating increased vitality.
The study also found that the combination of DOP and spermidine significantly reduced lipid accumulation in nematodes. In mice with metabolic disorders caused by a high-fat diet, the combination therapy markedly reduced body weight, blood sugar, triglycerides, harmful low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and total cholesterol levels, far exceeding the effects of individual treatments.
Metabolomic analysis revealed that the combination of DOP and spermidine regulated a broader range of metabolites, achieving a synergistic effect greater than the sum of their individual contributions. The combination primarily affected lipid metabolism, with significant changes in metabolites such as glycerol phosphate, linoleyl glycerol, and docosapentaenoic acid. Furthermore, the combination therapy increased the levels of NAD+, a crucial molecule for aging, and its precursor NMN.
Thus, the “golden duo” of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide and spermidine not only extends lifespan but also regulates metabolism, helping the body combat aging. But how can we incorporate these components into our diet?
Dendrobium Officinale: As DOP is the decisive active component, we can consume Dendrobium officinale directly. This traditional Chinese herb can be consumed in various ways, such as fresh eating, decoction, tea brewing, wine soaking, paste making, and soup cooking. The common dosage for dried Dendrobium officinale is 6–10g, while the fresh form is 15–30g. Fresh Dendrobium officinale can be chewed directly or decocted for internal use. Additionally, it can be sliced and used for tea brewing, wine soaking, or added to soups and porridge for dietary supplementation. Many dietary supplements are available on the market, including food-grade Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide extracts, powders, juices, and health foods. The general recommended dosage is 1g per serving, two to three times a day.
Spermidine: Spermidine can be supplemented through daily diet or dietary supplements. Although there is no definitive recommended intake, many spermidine supplements on the market suggest a dosage of 20–30mg per day. If you prefer not to use supplements, dietary sources are also excellent options. Spermidine is primarily found in whole grains, seafood, nuts, mushrooms, dairy products, and fermented foods.
By combining these two powerful ingredients, we may be able to enhance their anti-aging effects and promote longevity. However, it’s important to note that the dosages used in the studies were based on nematodes and mice, so individual needs may vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen.