What is NADH?
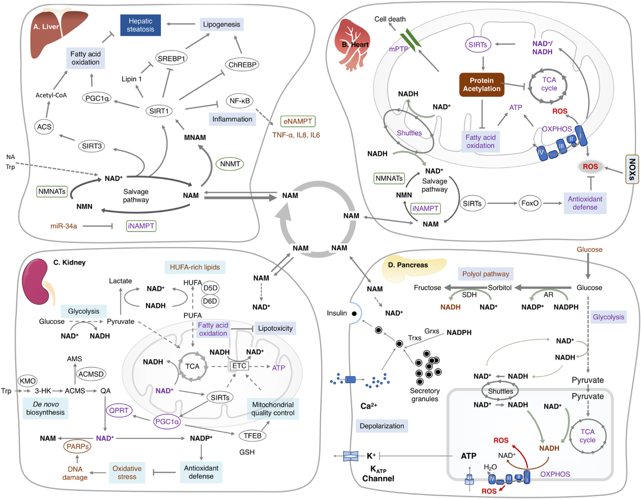
NAD + is an essential component of cellular processes necessary to support various vital metabolic functions. NADH(reduced form of nicotinamide adeninedinucleotide), is a crucial coenzyme in cellular respiration. NADH naturally exists in every cell and is involved in thousands of reactions. To emphasize its importance in life processes, scientists have named it the”Coenzyme No. 1 in the Human Body.” Additionally, because NADH plays asignificant role in the health of the “cellular engine” mitochondria, it is alsoreferred to as “Mitochondrial Factor.
The classic role of NAD + is a co-enzyme that catalyzes cellular redox reactions, while NADH is its reduced form in body, in many fundamental metabolic processes, such as glycolysis, fatty acid beta oxidation, or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In addition to playing these roles, NAD + has a critical role as the substrate of NAD +-consuming enzymes such as poly-ADP-ribose polymerases (PARPs), sirtuins, and CD38/157 ectoenzymes.
Reference:
[1]. Rex., A. et cl Pharmacology & Toxicology (2002) Vol 90, Issue 4, p220-225. Bioavailability of Reduced Nicotinamide-adenin-dinucleotide (NADH) in the Central Nervous System of the Anaesthetized Rat Measured by Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy
[2].Johnson., S. et cl. F1000Research (2018) 7 (F1000 Faculty Rev); 132. NAD+ biosynthesis, aging, and disease