Why NADH?
Scientifict researches have been shown that several different tissues and organs show decreases in NAD + levels over age, causing metabolic dysfunctions, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. This is a common phenomenon for human, mice, flies and many other animals. It has been shown that various diseases such as diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, retinal degeneration, depression and many more aging related symptoms.
A significant cause for this age-associated NAD + decline is the decrease in NAMPT-mediated NAD + biosynthesis. This age-associated decrease in NAD+ biosynthesis machinery causes a reduction in NAD + in a variety of tissues, affecting the activities of NAD +-dependent enzymes and redox reactions within the cell and leading to functional decline. Another cause for NAD + decline with age is the increase in NAD + consumption, and this is mainly due to the activation of PARPs .

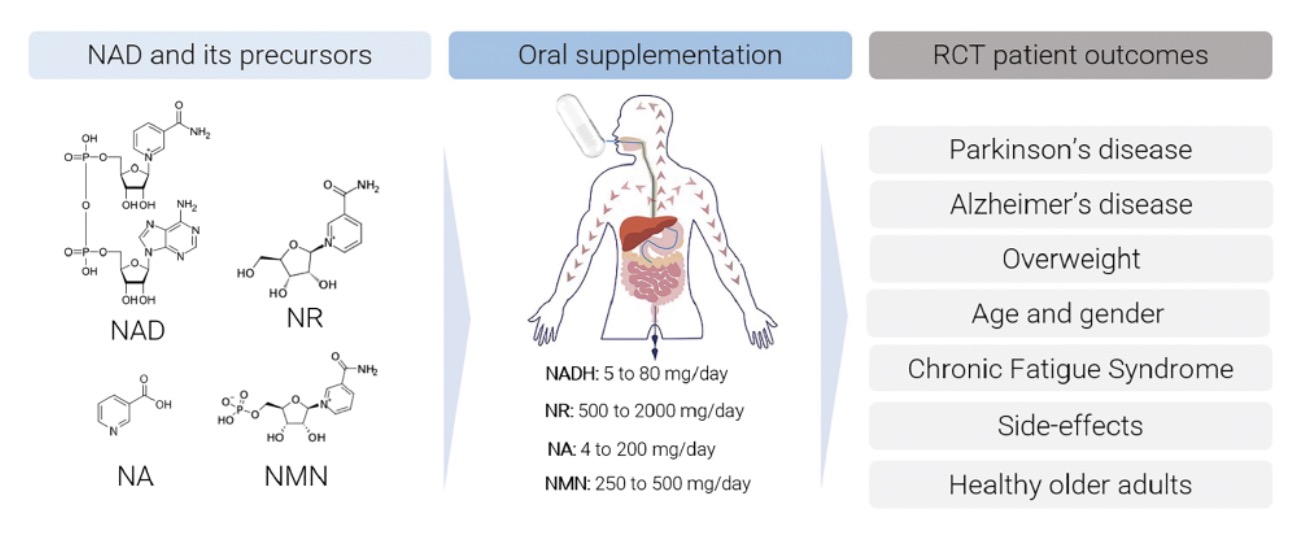
There are five major precursors and intermediates to synthesize NAD+: tryptophan, nicotinamide, nicotinic acid, nicotinamide ribodise (NR) and nicotinamide monomucleotide (NMN). Unlikely NADH, which could convert into NAD+ in a more efficient way, others have different route to convert to NAD+ , among which NMN has the shortest pathway. Thus, orally supplymen tof NADH is a more direct way of boosting NAD+ level in body regardless impairment of core NAD+ biosynthesis enzyme functions due to aging. It function direct to each aging cells, obtaining systematic function, and most importantly, being organic.
Meanwhile, scientific studies have shown that orall adiminstration of NADH, but not other NAD+ precusors, could significantly increase NAD+ level in animal cortex, which benefits for nervous systme health, fighting depression and many other neurological conditions such as Parkinson. Supplyment of NADH has shown benefits in early clinical trails for chronic fatigue syndrome, Parkinson’s disease, overweight, postmenopausal prediabetes, Alzheimer’s disease to improve quality of life, sleep quality, insulin sensitivity, decease in anxiety, anti-imflammation, with well-tolerated safety profile.
Reference:
[1]. Rex., A. et cl Pharmacology & Toxicology (2002) Vol 90, Issue 4, p220-225. Bioavailability of Reduced Nicotinamide-adenin-dinucleotide (NADH) in the Central Nervous System of the Anaesthetized Rat Measured by Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy
[2].Johnson., S. et cl. F1000Research (2018) 7 (F1000 Faculty Rev); 132. NAD+ biosynthesis, aging, and disease
[3] Alegre., J. et cl. Revista Clinica Espanola (2010) Vol 210, Issue 6, p284-288. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome
[4] Gindri., I. et cl. American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology & Metabolism (2024) Vol 326, Issue 4, pE417-427. Evaluation of safety and effectiveness of NAD in different clinical conditions: a systematic review